Technical Calculation of Power
In case of ball screw
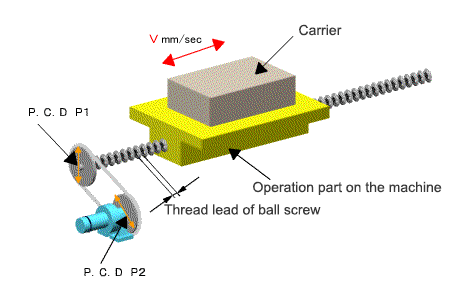 In the case of frequent start-stop operation, consider the load factor listed in a calalog.
In the case of frequent start-stop operation, consider the load factor listed in a calalog.Click here to refer the load factor listed in a catalog.
 In the case of frequent start-stop operation, consider the load factor listed in a calalog.
In the case of frequent start-stop operation, consider the load factor listed in a calalog.